2025-09-26
The main difference between honing and superfinishing lies in precision and surface quality. Honing is primarily used to correct geometry and remove material in controlled amounts, while superfinishing is a fine finishing process designed to achieve exceptionally smooth surfaces with low roughness and improved functional performance. In short, honing prepares the surface, and superfinishing perfects it.
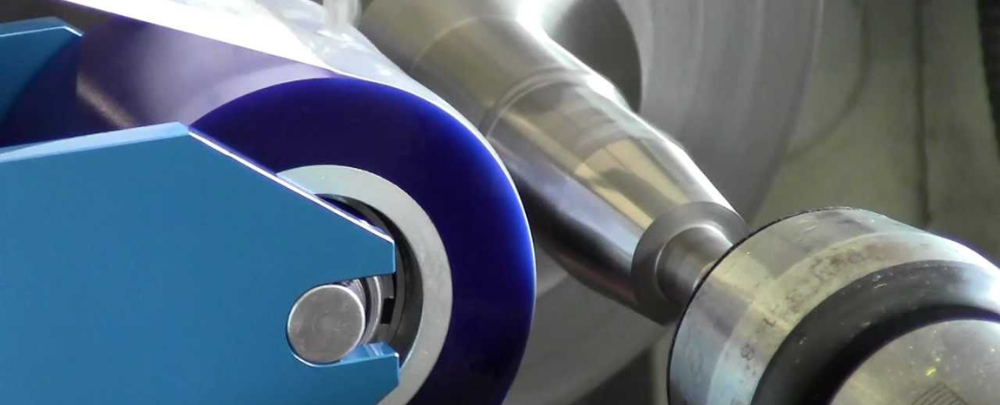

Honing: Improves dimensional accuracy, corrects shape errors (like out-of-roundness or taper), and creates a cross-hatch surface pattern for lubrication retention.
Superfinishing: Focuses on reducing surface roughness, removing the damaged surface layer, and improving bearing ratios for high-precision components.
Honing: Removes material in the range of 10–50 µm per pass, making it suitable for correcting errors and refining geometry.
Superfinishing: Removes only 1–2 µm, ensuring the geometry remains unchanged while eliminating micro-defects and achieving ultra-smooth finishes.
Honing Tools: Abrasive stones mounted on mandrels. Machines are designed to control feed, stroke, and pressure.
Super Finishing Machine: Uses fine abrasive films or stones with oscillating movement under low pressure. These machines are engineered for extreme precision and surface enhancement.
Honing: Produces a surface with Ra typically around 0.2–0.4 µm, with a cross-hatch structure that helps retain oil.
Superfinishing: Achieves Ra values as low as 0.01–0.05 µm, with a plateaued surface that minimizes friction and wear.
Honing: Cylinder liners, hydraulic sleeves, gears, and applications requiring oil retention.
Superfinishing: Bearing races, crankshafts, camshafts, and aerospace or medical components requiring mirror-like finishes.
| Aspect | Honing | Superfinishing |
Primary Purpose | Corrects geometry, improves dimensional accuracy, and creates cross-hatch texture | Enhances surface quality, reduces roughness, and improves bearing ratio |
Material Removal Rate | Higher (10–50 µm per pass) | Very low (1–2 µm or less) |
Surface Roughness (Ra) | Typically 0.2–0.4 µm | As low as 0.01–0.05 µm (mirror-like finish) |
Surface Texture | Cross-hatch pattern for oil retention | Plateau finish that minimizes friction and wear |
Tools Used | Abrasive stones mounted on honing mandrels | Fine abrasive films or stones with oscillating movement under low pressure |
Geometry Correction | Yes (fixes taper, roundness, and straightness errors) | No (only refines surface without altering geometry) |
Applications | Cylinder liners, hydraulic sleeves, gears | Bearing races, crankshafts, camshafts, aerospace and medical components |
Machine Type | Honing machine with controlled feed, stroke, and pressure | Super finishing machine designed for ultra-precision finishing |
Lubrication Effect | Improves oil retention due to cross-hatch grooves | Reduces lubricant film breakdown by smoothing asperities |
Industries | Automotive, hydraulic, heavy machinery | Automotive, aerospace, bearing manufacturing, precision engineering, medical devices |
Process Sequence | Usually performed before superfinishing | Typically performed after honing as a final finishing process |
A super finishing machine is indispensable in industries where performance, reliability, and durability depend on surface quality. By improving micro-geometry and removing residual stress, superfinishing extends component life and enhances energy efficiency in automotive, aerospace, and precision engineering applications.
Honing and superfinishing are not competing processes but complementary steps in achieving both accuracy and performance. Honing prepares the geometry and texture, while superfinishing brings the surface to perfection. For manufacturers demanding world-class quality, investing in a super finishing machine ensures components meet the highest standards of efficiency and durability.
 What Is Superfinishing Process?November 27, 2025The superfinishing process is a precision surface refinement method designed to remove the damaged layer left after grinding and achieve extremely low surface roughness — often reaching Ra ≤ 0.02 µ...view
What Is Superfinishing Process?November 27, 2025The superfinishing process is a precision surface refinement method designed to remove the damaged layer left after grinding and achieve extremely low surface roughness — often reaching Ra ≤ 0.02 µ...view Achieving Mirror-Like Surface Finishes: Super Finishing vs. Traditional MethodsSeptember 3, 2025When it comes to mirror-like surface finishes, traditional processes such as grinding, lapping, or polishing can only go so far. They remove material effectively but often leave directional marks, hea...view
Achieving Mirror-Like Surface Finishes: Super Finishing vs. Traditional MethodsSeptember 3, 2025When it comes to mirror-like surface finishes, traditional processes such as grinding, lapping, or polishing can only go so far. They remove material effectively but often leave directional marks, hea...view Comparing Wet vs. Dry Superfinishing Processes: Which Is Better?November 14, 2025In precision surface finishing, both wet and dry superfinishing processes can achieve excellent results — but they serve different purposes.Wet superfinishing provides superior heat control and longe...view
Comparing Wet vs. Dry Superfinishing Processes: Which Is Better?November 14, 2025In precision surface finishing, both wet and dry superfinishing processes can achieve excellent results — but they serve different purposes.Wet superfinishing provides superior heat control and longe...view Call us on:
Call us on:  Email Us:
Email Us:  No. 52-1 Zhang Road, Meicun Industrial Park, New District, Wuxi City, Jiangsu, China.
No. 52-1 Zhang Road, Meicun Industrial Park, New District, Wuxi City, Jiangsu, China.